India-Transport and Communication Sector
Classification of Transport and Communication
Land
1. Road
2. Railway
3. Pipe lines
Water
1. Inland
2. Oceanic
Air
1. Domestic
2. International
Land transport
Road transport
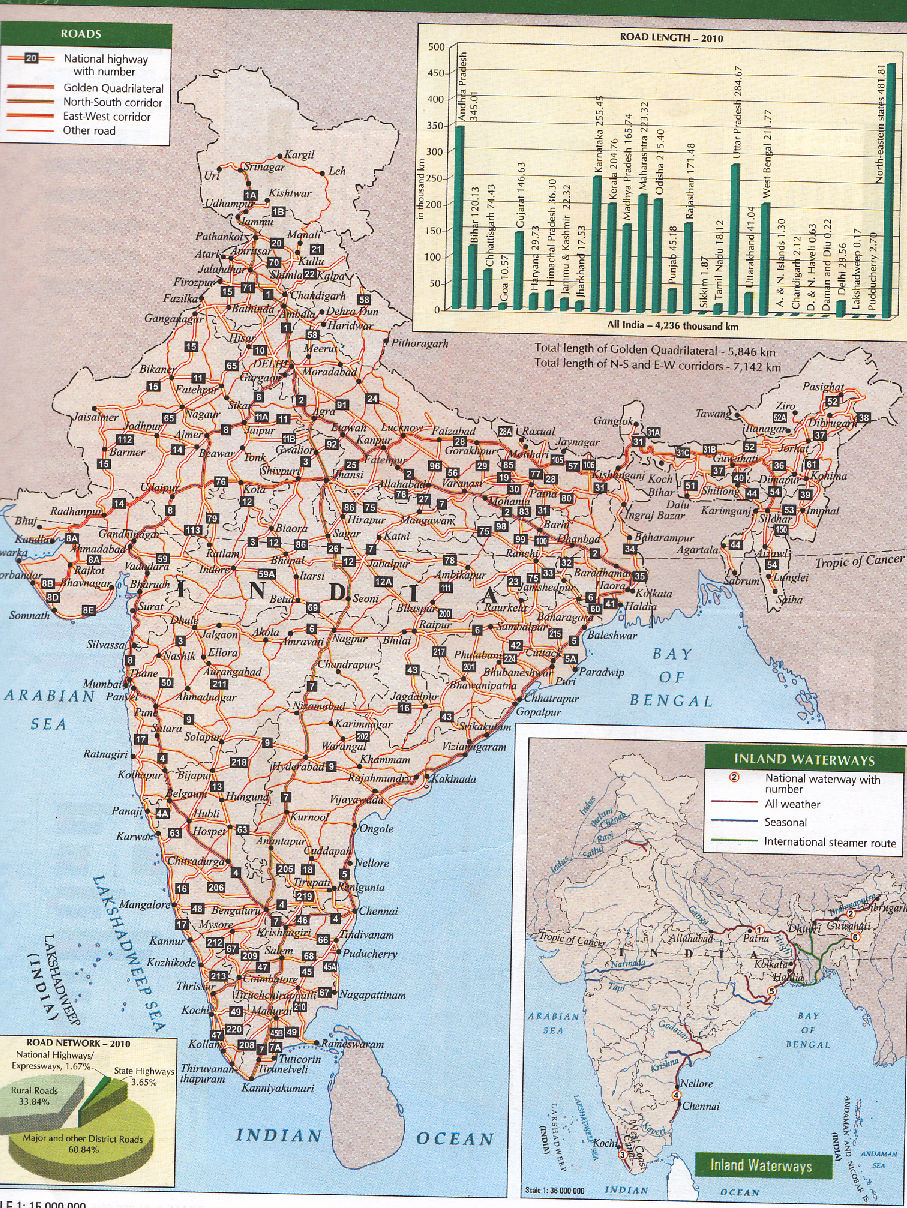
1. Total road length is 33.1 lakh km
2. 80% passengers, and 70% of freight are carried by roads
3. Shai road connect Indus valley to Sone valley
4. It is renamed as grad trunk road
5. At present it connects Amritsar, Kolkata (NH1 NH2)
Classification of Roads
I. National high ways
1. Constructed and maintained by central govt.
2. Meant for interstate transport
3. Movement of defense men and material
4. Connect state capitals
5. Total length is 65769 km
6. Accounts 2% of road length
7. Carry 40% of traffic
8. Golden quadrilateral 5846 km, 4/6/lane. High density traffic, connect metro cities, time
distance and cost distance decreased n-s corridor connect Srinagar to KanyaKumari
(4076 km) east west corridor connect Porbandar to Silchar (3640)
State High Ways
1. Constructed and maintained by state CPWD
2. Connect state capitals with Dist. Hqs.
3. Account for 4% of road length
District Roads:
1. Connect Dist. Hq with other towns
2. Account for 14% of road length
Rural Roads
1. Connect rural areas
2. Accounts 80% of road length
3. Regional variation in road density
4. Influenced by terrain and climate
Other Roads
Border Roads and International Highways
1. BRO was started in 1960
2. Help to develop economy
3. Strengthen the defense
4. Improvement of strategic points
5. It is a premier multifaceted ted construction agency
6. Highest road way connects Manali –Leh with4270 mts. altitude
7. Maintain harmoniousrelation with neighboring countries
Highest road density is 387.24 /100sq.km in Kerala lowest road density is 10.48 /100 sq. km
in J&K it is high in northernplains and low in mountain areas
Factors influence in road ways
1. Terrain
2. Climate
3. Economic development
4. Industries
5. Cities and towns
Railways:
1. The first railway line started in 1853 between Bombay and thane
2. It is the largestgovt. Sector with the length of 63221 km
3. It is divided into 16 zones
1. Northern – New Delhi
2. North Eastern – Gorkpur
3. NE frontier –Maligoan
4. N. Western- Jaipur
5. N. Central- Allahabad
6. Western ChurchGate Mukbai
7.W. Central – Jabalpur
8. Central CSTMumbai
9. E. Central –Hajipur
10. Eastern-Kol
11. S. Western –Hubli
12. S. Central- Seceuderabad
13. SE Central-Bilaspur
14. Seastern-Kolkota
15. Southern Chennai
16. East Coast- BBSR
2. Highest coal is carried by railways
3. Railway Gauges: broad gauge: 1.676 mts. 46807 km 74.145-meter gauge: 1.000 mts.
13290 km 21.02% narrow gauge 0.672mts and 0.610 mts. 4.94% 3124 km
Recent Developments in Railways:
1. Conversion of meter and narrow gauges in to broad gauge
2. Stem engines are replaced by diesel and electrical engines
3. Introduction of metro railways
4. Use of CNG
5. Introduction of internet
6. Computer reservation
7. Container services
Water Transport
Advantages
1. Cheapest means of transport
2. Least consumption of energy
3. Suitable for heavy bulky goods
4. No friction
5. Eco friendly
6. There are two types
Inland Water Ways
1. Cheapest mode of transport
2. Competition from road ways and railways
3. Water diversion fromthe rivers cause less navigable
4. Total 14500 km of navigable water
5. Account 1% of transport
6. It consists of rivers, canals, backwaters creeks
7. 3700 km of navigable rivers are available
8. 2000 km actually used
9. Canals are controlled by inland water way authority
10. There are three inland waterwaysin India
1. NW Allahabad to Haldia – 1620 km most important waterway, up to Patna mechanized
boats and up to Hardwarmanual boats
It is divided in to three segments: 1. Haldia to Farakka 560 km 2. Farakka to Patna 460 km
3. Patna to Allahabad 600 km
2. NW-2 Sadiya to Dubri891 km steamers can travel up to Dibrugarh
3. NW -3 Kottapuram to Kollam 205 kmit includes 168 km west coast canal and Udyoga
mandal canal
Back waters of Kerala also important waterways.
Ocean Route: India has coastline about 7517 km there are 12 major ports and 185 minor
ports
95 % of India foreign trade and 70 % of valueis trade takes place through sea ways
Air Transport
Advantages
1. Fastest means of transport
2. Connect remote areas
3.no need to maintain routsand construct
4. Suitable for emergency times
5. All continents are connected by air ways
6. Suitable for difficult terrain
7. Reduce travel time
8. Maintained by airport authority
9. It maintains 126 minor airports 11 international air ports and 86 domestic airports
10. 29 civil defense enclavesin defense service also maintained by the authority
There are three divisions
1. Air India: provide international air services
2. Connects all continents
3. Delhi and Mumbaiair ports accounts for 52% of air service
Indian airlines connect Indian subcontinent
It is the part of air India
Pawan Hans helicopter services
serves in north eastern states
Pipelines:
Advantages:
1. Most convenient and efficient mode of transporting liquids and gases over longdistance
2. Least consumption of energy
3. Suitable for mountain areas and sea bottom
4. Asia’s cross country pipe line is constructed between Naharkatia oil field and Barauni
oil refinery with the length of 1157 km, it was extended up to Kanpur in 1966
5. Other pipe lines Are Ankaleswar to Koyali, Mumbai High to Koyali Hazira Vijaipur
Jagdishpur
6. Salaiya to Mathura – 1256 km
7. Numaligarh to Siliguri 660km
Communication: It is divided into personal- mobile mass radio, TV.
Personal communication has become most important at present.
User can contact with the customer directly. Fastest means of communication.
Communication revolution came into world through internet.
Mass communication consists of radio, tv and satellite communication.
Satellite communication is the recent development most useful at the time of emergency.
When all other communications are failed it is the only communication which can be used.



Comments
Post a Comment